What Is an Echocardiogram? Your Friendly, No-Stress Guide to Seeing Your Heart in Motion
If your doctor ordered an “echo,” you’re not alone — millions of people have this safe, painless test every year. But what exactly is it? Why do you need it? And what will happen during the test? Let’s break it all down
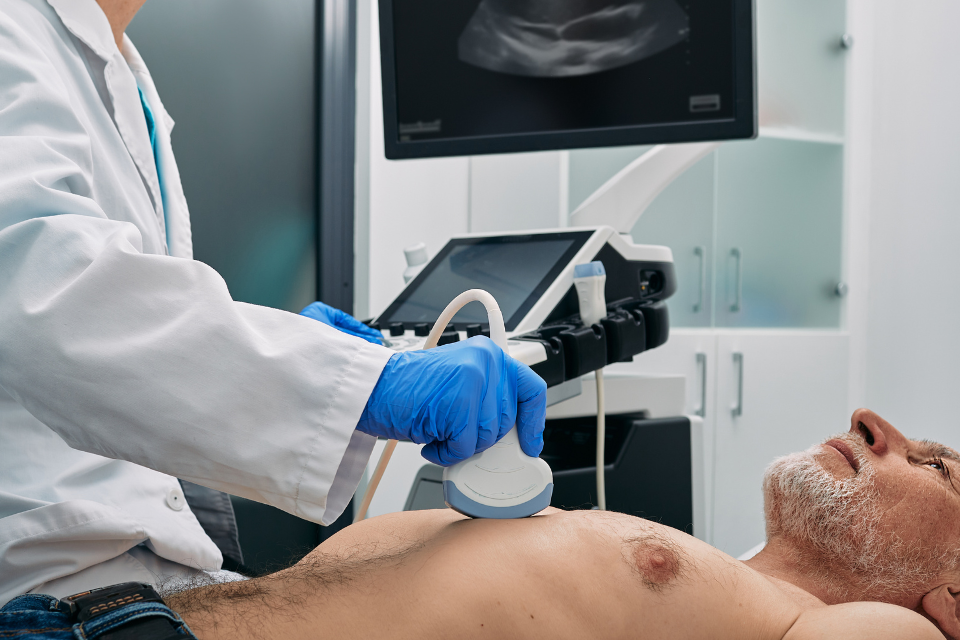
❤️ What Is an Echocardiogram?
An echocardiogram (often called an “echo”) is a special type of ultrasound scan that creates live, moving pictures of your heart using harmless sound waves — just like the ones used to see a baby during pregnancy.
✔️ The size and shape of your heart’s chambers
✔️ How your heart valves are opening and closing
✔️ Whether there’s fluid around your heart
✔️ Signs of damage from a prior heart attack or high blood pressure
📊 Why Would You Need an Echo?
Your doctor may recommend an echocardiogram if you have:
- Shortness of breath or fatigue (especially with activity)
- Swelling in your legs or abdomen
- Heart murmur (an unusual sound heard with a stethoscope)
- Chest pain or suspected heart failure
- History of heart attack, valve disease, or congenital heart defects
- Before or after heart surgery
- To monitor conditions like high blood pressure or cardiomyopathy
It’s also used to: 🔹 Diagnose the cause of irregular heartbeats
🔹 Check how well treatments (like medications or devices) are working
🔹 Evaluate heart function in cancer patients receiving certain chemotherapies
During a standard transthoracic echocardiogram (TTE) — the most common type — here’s what happens:
- You’ll lie on your left side on an exam table.
- A technician (called a sonographer) will place small sticky patches (electrodes) on your chest to monitor your heartbeat.
- They’ll apply a cool, water-based gel to your chest.
- Then, they’ll gently press a small handheld device called a transducer against your skin. It sends and receives sound waves.
- The sound waves bounce off your heart and create moving images on a screen — which are recorded for your doctor to review.
⏱️ The test takes 30–60 minutes. You can breathe normally and talk during the test — no pain, no needles, no radiation.
📈 What Does an Echo Measure?
Your cardiologist will look at several key things:
🔹 Ejection Fraction (EF) — The percentage of blood your left ventricle pumps out with each beat. Normal is 50–70%. Lower numbers may mean heart failure.
🔹 Valve Function — Are your valves opening fully? Leaking? Too tight?
🔹 Wall Motion — Is every part of your heart muscle squeezing normally?
🔹 Chamber Size — Enlarged chambers can signal high blood pressure or valve problems.
🔹 Pericardium — The sac around your heart. Is there fluid buildup?
🆚 Types of Echocardiograms
Not all echoes are the same. Here’s what you might encounter:
- Transthoracic Echo (TTE) — Standard echo through the chest wall. Most common.
- Transesophageal Echo (TEE) — A thin probe is gently passed down your throat to get ultra-clear images. Used when TTE isn’t clear enough — like for evaluating clots or complex valve disease. You’ll be sedated.
- Stress Echo — Done before and after exercise (or medication-induced stress) to see how your heart responds under pressure. Great for detecting hidden blockages.
- Doppler Echo — Measures speed and direction of blood flow — helps detect valve leaks or narrowed arteries.
- 3D Echo — Creates 3-dimensional images for surgical planning or complex anatomy.
🚫 Risks? Almost None.
✅ TTE (standard echo): Zero risks. Completely safe for everyone — including pregnant women and children.
✅ Stress Echo: Very low risk — same as a regular stress test.
⚠️ TEE: Mild discomfort or sore throat afterward. Rarely, minor bleeding or reaction to sedation.
✅ Doppler & 3D: No added risk — just extra features on the standard echo.
🧑⚕️ What Happens After the Test?
- A cardiologist will review the images and measurements.
- Results are usually ready in 1–3 days.
- Your doctor will explain what the echo showed — and what it means for your health.
- If something abnormal is found, they’ll discuss next steps — which could include medication, lifestyle changes, further testing, or referral to a specialist.
Pro tip: Ask for a copy of your echo report and keep it in your personal health file — especially your ejection fraction. It’s a key number you’ll want to track over time.
💬 Real Patient Story
“I kept getting tired climbing stairs. My doctor ordered an echo and found my heart was only pumping at 35%. I started medication — and within months, my energy came back. That echo literally gave me my life back.”
— James, 61
✅ Final Thought
An echocardiogram is one of the most powerful — yet gentle — tools in heart care. It doesn’t just show your heart… it shows how your heart lives and moves. And that information can guide life-saving decisions.
So if your doctor says, “Let’s get an echo,” breathe easy. You’re taking a smart, safe step toward understanding — and protecting — your heart.

